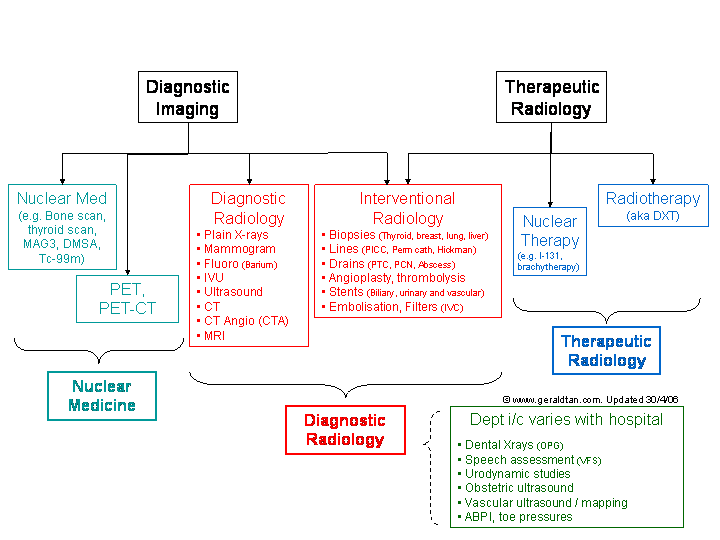
Organisational chart of imaging departments (aka Which department do I arrange this scan with?)
CONTENTS |

However, most of the hospitals don’t have all three departments. For some scans, they will be
done by the radiology department; for others, the patient will have to travel
to another hospital. |
| Who is he? | His role | When you need to look for him! | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiologist | Medical doctor specialising in imaging | ||
Doesn’t actually do most scans! (except fluoro, U/S and angio) |
|||
| Radiographer | Technologist who runs the xray machines(Diploma holder after ‘A’-level) | ||
| Sonographer | Specialised radiographer that does ultrasound | ||
| Clerk | Runs the front desk! | ||
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Plain Xrays | ||
| i/v contrast: -CT -IVU |
||
| Ultrasound | - | - |
| MRI |
Depending on model/operation date | |
| Barium swallow / meal / enema |
(use water-soluble contrast) |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Plain Xrays | No | |
| Mammogram | No | Ideally in first 14 days of menses (will be arranged by the appt desk) |
| Ultrasound | For HBS and renal arteries | |
| Barium swallow / meal | Yes | |
| Barium enema | Yes, overnight | Bowel preparation 1-2 days before |
| IVU | Yes | Bowel preparation 1-2 days before |
| CT abdomen &/or pelvis | Yes | May require oral contrast 1-2 hours before |
| MRI | For liver, MRCP |
|
Risk from radiation is a
slope, there is no one “cut-off” point below which it is “perfectly safe” - even
small radiation doses may have some risk. Therefore, statutory regulations
require the dose to be “as low as reasonably achievable”.
Having said that, there is no absolute “legal” limit to the dose a patient can receive - go ahead and order the scan if you think the investigation is medically indicated, and the benefits outweigh the risk. What then, is the risk, and how do you explain it to patients in layman terms? |
| Modality / Procedure | Equivalent of “normal” daily background radiation |
Risk of fatal cancer / death |
|---|---|---|
| Xray – Limbs | 1 day | 0.0001% (1 in a million) |
| * Eating 2 bananas a week for 1 year | 1 day | |
| Xray – CXR | 3 days | 0.0003% |
| Xray – Skull | 9 days | 0.001% (1 in 100,000) |
| * Smoking 1 pack of cigarettes | - | 0.001% |
| * Flight from Singapore to New York | 1 month | |
| Mammogram | 2 months | 0.005% |
| Xray - Abdomen, Pelvis, Spine | 4 months | 0.01% (1 in 10,000) |
| Tc-99m thyroid scan | 6 months | |
| IVU | 1 year | 0.03% |
| Barium swallow, meal, follow-through | 1 – 1.5 years | 0.03% |
| CT Head | 10 months | 0.03% |
| Tc-99m dynamic cardiac scan | 2 years | 0.05% |
| CT Chest, abdomen or pelvis | 3.5 years | 0.1% (1 in 1,000) |
| * Dying in a home accident each year | - | 0.1% (1 in 1,000) |
| * Smoking 1 pack of cigarettes a day x 1 year | - | 0.35% |
|
(1) Allergic reaction / anaphylaxis
- Idiosyncratic, just like all other drugs - Increased risk if (1)Multiple drug allergies (2)Recent asthma (<1 year ago) - Prevention: Steroids given AT LEAST 12 hours before the scan. - Examples are : Prednisolone 20mg the night before and on the morning of the scan. - In emergencies: Hydrocortisone i/v 200mg q4h starting at least 6 hours before the scan. (2) Extravasation - Definition: When the contrast is forced outside the vein - Background: About 50mls of contrast (which is as viscous as D50%) is injected as fast as 5mls/second under great pressure (If you don’t believe, get a 20ml syringe, some D50%, a blue plug, and see if you can inject everything out in 5 seconds!!). - Problem: Vein bursts (damn, got to reset the plug ;-) --> Contrast leaks out into tissue --> Draws water from surrounding tissues --> (1)Dehydration (& cell death)of surrounding tissues and (2)Compartment syndrome - Prevention: - i. Make sure plug works(They check, and you’ll just have to walk down to the department to re-set it if it doesn’t work) - ii. Large bore (Pink/Green) plug for procedures requiring high-injection rates (generally anything vascular/arterial). - iii. If all else fails, blue plugs (but not in tiny finger veins!) may be acceptable for slow-injection rates (e.g. brain) - iv. PICCs are NEVER acceptable. (1) The tiny tip can blast off into the pulmonary arteries and (2) SVC rupture is not a pretty sight. - Treatment: - i. RICE (Rest, Ice-pack, Compress, Elevate extremity) - ii. Watch for compartment syndrome, especially if large volume (3) Contrast induced nephrotoxicity - Defined as a 25% increase in serum creatinine (does not always require dialysis though). - 1% in low risk patients - 10% in high risk patients (Diabetes, CCF, renal impairment, nephrotoxic drugs, age > 70yrs) - Prevention: - i. Any high risk factors: Pre-hydrate patient - ii. Renal impairment: Consider N-acetylcysteine (600mg bd x 2 day before and on day of scan) - iii. Space out contrast studies 72h apart, if possible (e.g. cancer staging) - iv. Consider non-contrast CT or alternate studies (e.g. US, MRI) - Paradoxically, patients whose kidneys have already failed and are on dialysis can ignore all the above. (4) Metformin-induced lactic acidosis - Metformin: Stop on the day, and 2 days after the scan. - Once again, do this proactively, if you think patient might be going for a contrast-CT soon! (Just don’t forget to convert to insulin/another OHGA, and to re-start it later!) (5) Breast feeding - Can scan as per normal, but no breast feeding x 24h after the scan |
| FAQ |
| Indication | Investigation |
|---|---|
| Vault # | Skull (AP,Lateral, Towne’s) |
| Maxilla # | Skull (AP, Lateral, OM) |
| Mandible # | Mandible X-xray |
| Orbit # | Orbit X-ray |
| Orbital foreign body | Orbit X-ray + Look up/down views |
| Sinusitis (chronic) | X-ray Paransal sinuses |
| Indication | Investigation |
|---|---|
| FB Throat | Neck xray,lateral (not C-spine) |
| Cervical spine trauma | C-spine xray (not Neck)
+/- Swimmer / Lat pull-down for C7/T1 |
| Parotid stone | Parotid xray (occlusal view) |
| Dental | Occlusal / OPG |
| Indication | Investigation |
|---|---|
| Swallowing assessment / ?Aspiration | (1)VFS if high % aspiration (2)Barium swallow (not gastrograffin) |
| FB throat / perforation / post-esophagect | (1)Gastrograffin swallow (2)NB: CT neck better for FB |
| Nasolacrimal duct stenosis | Dacrocystogram* |
| Salivary/Parotid duct stenosis | Sialogram* |
| Indication | Investigation |
|---|---|
| Thyroid lump / goitre | U/S thyroid |
| Young CVA | U/S carotids |
| Indication | Investigation | Contrast? |
| Stroke, hemorrhagic Head injury (see NICE criteria) | CT brain | No |
| Meningitis | CT brain | Maybe |
| Fits, brain tumour, mets | CT brain | Yes |
| Chronic sinusitis | CT paranasal sinuses | No |
| Hearing loss, conductive | CT temporal bone | No |
| Foreign body throat | CT neck | Maybe |
| Indication | Investigation | Contrast? |
| Stroke, hyperacute (< 12 hours) |
MRI brain (stroke
protocol) NB: CT is better to exclude bleed |
No |
| Stroke, brainstem Posterior fossa lesions | MRI brain (more sensitive than CT) | Maybe |
| Hearing loss, sensorineural | MRI IAM / MRI IAM screening | Yes |
| Retrobulbar mass, orbital tumor | MRI orbits | Yes |
| Indication | Investigation | Which side? |
|---|---|---|
| Basic CXR view | CXR (Erect) | |
| Rib # | CXR (Oblique) | Same side as suspected # i.e. R oblique for R # |
| Localise lung lesion | CXR (Lateral) | Same side as lesion |
| Loculated effusion, or patient cannot sit up | CXR (Lateral decubitus) | Same side as effusion i.e. R LD for R effusion |
| Small pneumothorax, or patient cannot sit up | CXR (Lateral decubitus) | Opposite side of pneumothorax i.e. R LD for L pneumothorax |
| Sternal # | Sternal Xray |
| Indication | Investigation |
|---|---|
| Diaphragmatic paralysis | Fluoroscopic sniff test* |
| Indication | Investigation | Contrast |
|---|---|---|
| Most lung conditions | CT Thorax / CT Chest | |
| Interstitial lung disease | High resolution CT (HRCT) (NB: Slices are “skipped” – do not use for tumour detection) | No |
| Aortic aneurysm / dissection | CT Aortogram / CT Thoracic aorta | Yes (High rate) |
| Pulmonary embolism (PE) | CT PE / CT Chest (PE protocol) | Yes (High rate) |
| Coronary arteries | CT Coronary Arteries / Cardiac CT | Yes (High rate) |
| Indication | Investigation |
|---|---|
| Standard AXR view | AXR (Supine) |
| Air-fluid levels | AXR (Erect) or (Lateral decubitus) |
| Free air under diaphragm | CXR (Erect) or (AP Sit) |
| Ureteric/bladder calculi | KUB |
| Indication | Investigation | Preparation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver, gallbladder | U/S liver / HBS | Fast x 8 hours | Includes a quick look at kidneys |
| Kidneys | U/S kidneys | - | |
| Kidneys & bladder | U/S kidneys + bladder | Needs to have a full bladder | Not routinely ordered |
| Renal arteries | U/S renal artery | Fast x 8 hours | Specialised investigation |
| Aorta | U/S abdominal aorta | Fast x 8 hours | CT preferred, if possible |
| Uterus/ovaries | U/S pelvis | Needs to have a full bladder | May include endovaginal scan |
| Testes | U/S testes | - |
| Indication | Investigation | Preparation |
|---|---|---|
| Hydronephrosis, ?stones | IVU | Fast overnight, bowel prep |
| Indication | Investigation | Requirements | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Esophagus / swallowing problem | Barium swallow | Be able to stand | |
| Stomach / PUD / reflux / hiatus | Barium meal | Be able to stand and roll over. | |
| Small bowel pathology | Barium follow-through | ||
| Enteroclysis | More invasive than follow-through, but better results | ||
| Large bowel | Barium enema | Be able to stand and roll over. No fecal incontinence. | |
| ?anastomotic leak | Water-soluble / gastrograffin swallow/ meal/ enema. | As for similar barium study. | Include op details (incl anastomosis type), and exact date study is required on form. |
| Urethral stricture | Ascending urethrogram | Include op details if any | |
| Vesico-ureteric reflux | MCU | Include op details if any | |
| Post PCN | Check nephrostogram |
| Indication | Investigation | Contrast |
|---|---|---|
| Upper abdominal pathology | CT abdomen | Yes |
| Pelvic / gynae pathology | CT pelvis | Yes |
| Entire abdominal cavity required | CT abdomen + pelvis (abdo/pelvis) | Yes |
| Liver (Routine e.g. abscess) | CT liver | Yes |
| Liver lesion ?HCC | CT liver (triphasic) | Yes (High rate) |
| Liver HCC post-TACE | CT liver (plain + triphasic) | Yes |
| Pancreas | CT pancreas (fine cuts) | Yes |
| Renal /ureteric stone | CT KUB (may differ by hospital) | No |
| Kidneys | CT kidneys | Yes (High rate) |
| Kidneys, ureter, bladder | CT urogram(may differ by hospital) | Yes (High rate) and Lasix |
| Abdominal aorta | CT abdominal aorta | Yes (High rate) |
| Colon | CT colongraphy | Yes and rectal gas |
| Indication | Investigation | Contrast |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | MRI liver | Yes |
| Bile duct stones | MRCP | Maybe |
| Pancreas | MRI pancreas | Yes |
| Kidneys | MRI kidneys | Yes |
| Indication | Investigation | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Screening | Mammogram | |
| Evaluation of breast lump | Ultrasound + Mammogram | |
| Biopsy of lump | Ultrasound guided bx | Specialised investigation |
| Biopsy of lesion on mammogram | Mammotome / Stereotactic biopsy | Specialised investigation |
| Implant rupture | MRI breast | Specialised investigation |
|
Skull
Spine Upper limb Pelvis Lower limb |
| Indication | Investigation |
|---|---|
| Rotator cuff pathology | U/S shoulder |
| Carpal tunnel, cysts, neuroma | U/S wrist |
| DDH / CDH (< 4-6 mths) | U/S hip |
|
|
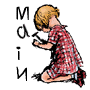
Read the following before using this page! |
 |
 |
 |